For example, John Smith may own a landscaping company called John Smith’s Landscaping, where he performs most — if not all — the jobs. Net value refers to the umbrella term client heartbeat with xero that a company can keep after paying off all liabilities, also known as its book value. It specifically highlights the amount of ownership that the business owner(s) has.
What Is a Liability in the Accounting Equation?
On 1 January 2016, Sam started a trading business called Sam Enterprises with an initial investment of $100,000. For every business, the sum of the rights to the properties is equal to the sum of properties owned. Unearned revenue from the money you have yet to receive for services or products that you have not yet delivered is considered a liability. To learn more about the balance sheet, see our Balance Sheet Outline.
The accounting equation And how it stays in balance

The accounting equation is important because it allows the business or entity to correctly record transactions and, therefore, maintain their financial statements. Liabilities refer to debts or obligations owed by the business. They are a particular amount owed to creditors of the business. Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, bank loans, and taxes.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage. These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation.
For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability. The accounting equation relies on a double-entry accounting system. In this system, every transaction affects at least two accounts.
- With the accounting equation expanded, financial analysts and accountants can better understand how a company structures its equity.
- To further illustrate the analysis of transactions and their effects on the basic accounting equation, we will analyze the activities of Metro Courier, Inc., a fictitious corporation.
- That’s why you’re better off starting with double-entry bookkeeping, even if you don’t do much reporting beyond a standard profit and loss statement.
- One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity).
- The accounting equation matters because keeping track of each transaction’s corresponding entry on each side is essential for keeping records accurate.
At first glance, this may look overwhelming — but don’t worry because all three reveal the same information; it just depends on what kind of information you’re looking for. Still, let’s dive into the differences between the two so that you can understand how each might affect your bookkeeping process. This simple, easy-to-understand tool can tell you what you need to know upfront so you know what to focus on if there are any issues or room for improvement.
So, let’s take a look at every element of the accounting equation. Cash (asset) will reduce by $10 due to Anushka using the cash belonging to the business to pay for her own personal expense. As this is not really an expense of the business, Anushka is effectively being paid amounts owed to her as the owner of the business (drawings). The cash (asset) of the business will increase by $5,000 as will the amount representing the investment from Anushka as the owner of the business (capital). Owner’s or stockholders’ equity also reports the amounts invested into the company by the owners plus the cumulative net income of the company that has not been withdrawn or distributed to the owners.
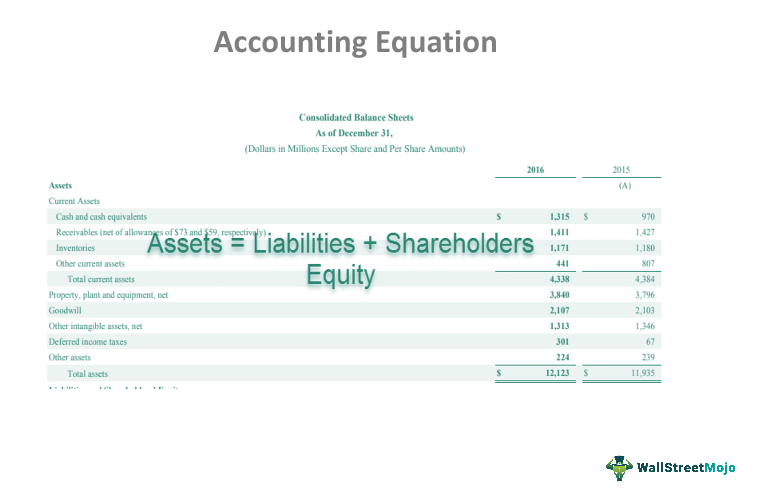
As its name implies, the Accounting Equation is the equation that explains the relationship of accounting transactions. The Accounting Equation states that assets equals the total of liabilities and equity. At the same time, it incurred in an obligation to pay the bank. When the total assets of a business increase, then its total liabilities or owner’s equity also increase. We know that every business holds some properties known as assets. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business.
